Air Compressors are used across different industries and company sizes. There are two types of air compressors, Piston or Reciprocating Compressors and Rotary Screw Compressors. Both work relatively the same way. They create compressed air by mechanically squeezing air to reduce its volume.
Each design has its way of achieving the end goal of compressed air. The question is which one would work best for your particular situation.
What is a Piston (Reciprocating) Air Compressor?
A Piston Air Compressor, also known as a Reciprocating Compressor, compresses air by using pistons driven by a crankshaft. This compressor is perfect for many general uses and is the most common type used in automotive services. Not only are they efficient, but maintenance is also easy.
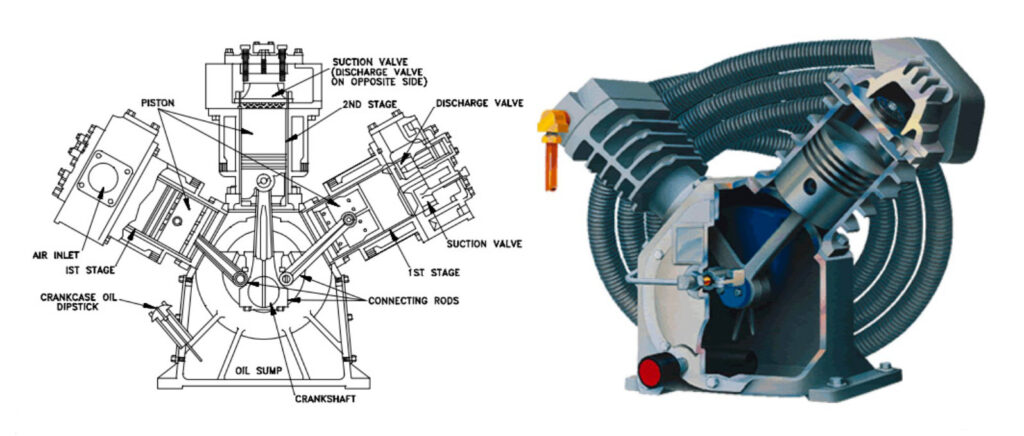
When would you use a Piston Air Compressor?
Piston Air Compressors are designed to run intermittently, for instance, 20-30% duty cycle. This would be acceptable for applications where short bursts of air are needed. Businesses that have a lower demand for compressed air would benefit from a Piston Air Compressor.
Related: Benefits of oil-free air compressors
Applications for piston air compressors include:
- Small machine shops
- Tire shops
- Airbrushing
- Sandblasting
- Construction work
- Residential usage
- Blow-off for cleaning
- Manual power tools
- Manual applications
What is a Rotary Screw Air Compressor?
A Rotary Screw Air Compressor creates compressed air by using two meshing helical screws called rotors. Air is forced through chambers as the interlocking spirals turn, pushing the air into a smaller space, thereby compressing it. This is a continuous process, as a Rotary Screw Air Compressor is designed to run all the time.
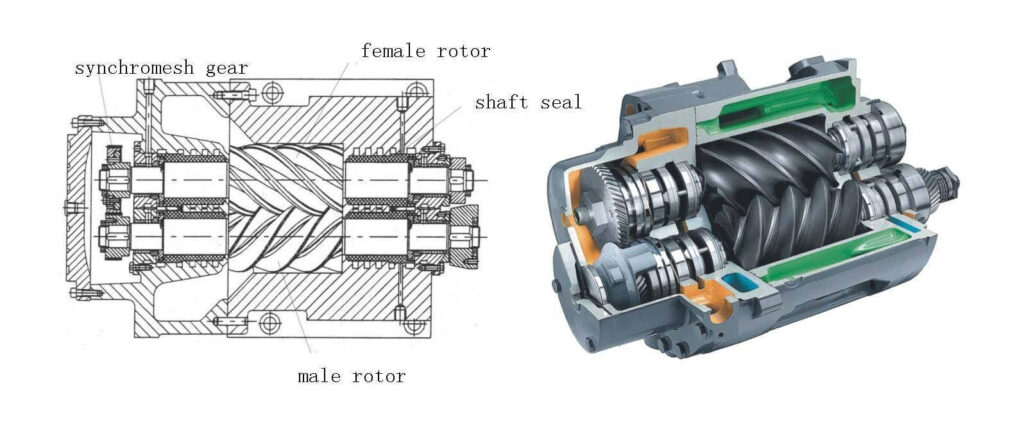
This type of system is fluid cooled. This fluid helps clean contaminants from the compressed air, keeps the bearings in the pump lubricated, helps to keep the system cool, and creates a seal extending the life of the rotors and casing.
When would you use a Rotary Screw Air Compressor?
A Rotary Screw Air Compressor is not made for intermittent use and could be damaged by not being used enough. They need to be used as close to their full capacity as possible. So basically, 100% duty cycle is what these compressors are designed for.
Applications for rotary screw air compressors include:
- Food Processing and packaging
- High-volume manufacturing
- Robotic manufacturing
- Conveyor systems
- Paint production lines
- Hospitals
- Applications requiring very clean air
- Collision repair
- Industry that needs continuous compressed air
Related: Benefits of Onsite Nitrogen Generators
Pros and Cons of Piston vs. Rotary Screw Air Compressors
Naturally, there are pros and cons to each of these systems. Here is a breakdown of each to give you a better idea of which one your company might need.
Piston Air Compressor Pros
- Initial capital investment is relatively low
- It can be operated in a dirty environment (indoors or outdoors)
- Maintenance is simple and less expensive
- Can run intermittently without causing any damage
- You will get better energy efficiency for low CFM
Piston Air Compressor Cons
- Piston compressors are very noisy
- They run hot, producing a lot of hot air
- Overall life expectancy is lower
- You will see a high oil carryover
- They are not always reliable
Rotary Air Compressor Pros
- Produces cleaner air
- You will get better energy efficiency for high CFM
- There will be less oil carryover
- They have a cooler internal operating temperature
- They operate continuously
- More quiet operation
- These offer high reliability
- Rotary compressors last longer
- Higher CFM per horsepower
Rotary Air Compressor Cons
- You can expect a higher initial capital investment
- They need a clean operating environment
- Regular maintenance by a skilled technician is required
What Type of Air Compressor Should I Use?
Your decision on which air compressor type you need depends partly on the amount of compressed air you need to produce, how often you need it produced and what you are using your compressed air for. The environment you will be using your compressor in will also matter.
What to consider when choosing the right air compressor
Consider the noise level
A Piston Air Compressor is very noisy and creates so much vibration that it may need to be bolted to the floor. You may not be able to have it inside your shop because of the racket it makes. You could put it outside or build a separate room for it, but often it ends up in a less than ideal area. If you end up having to place it in a hot room, this can affect operating temperature, so where you install it will affect the air quality and the compressor’s life.
A Rotary Air Compressor is so much quieter that your employees can still carry on normal conversations nearby. This means you can install them right where you need them, close to the action, without hindering performance.
Consider the temperature levels
A Piston Air Compressor runs at an internal temperature of between 300 to 400 degrees. The hotter your compressed air is, the more moisture it will hold. That can mean you will need additional equipment to dry and clean the air.
A Rotary Air Compressor runs at an internal temperature of between 170 to 200 degrees, which is much cooler than the Piston Compressor. A Rotary Compressor features aftercoolers and a powerful fan which helps to lower temperatures.
Consider Maintenance
A Piston Air Compressor requires routine maintenance such as inlet air filters, drive belts, and oil. Although these are inexpensive and easy to maintain, eventually, as cylinders, pistons, and other components wear down, the system will produce less and less air. It will finally require major services such as needing to be rebuilt or replaced.
Related: Air Compressed Systems Maintenance Tips During Summer
A Rotary Screw Compressors have higher recurring service costs but fewer moving parts, so they are more reliable and last longer. Since the rotors do not touch, they will not wear down. This system has fluid in it that acts as a protectant, extending the pump’s life, making the compressor last longer.
Related services: Preventive Maintenance
Consider the price
Although a Piston Air Compressor initially costs less, the comparison of cost extends past the initial transaction. Rotary compressors may cost more initially but they can save you money in the long run. A pre-owned air compressor can also help to keep your costs down.
There are many factors to consider when choosing the best air compressor for your shop or manufacturing plant.
Which compressor will save your company the most time and money in the long run?

